Chemicals for hot-dip galvanising from a single source
Pre- and post-treatment in a hot-dip galvanising plant plays a crucial role in the quality of galvanised surfaces. Continuous improvement is always the focus of galvanisers, not least in terms of competitiveness.
The application engineers at STOCKMEIER Chemie always consider the complete process and work with you to develop overall concepts. Cost-effectiveness, efficiency, sustainability and environmental friendliness are always at the forefront.
For over 40 years, the Surface Technology department has been dealing with the field of hot-dip galvanising and continuously developing the numerous existing products and processes for pre- and post-treatment. As a result, our own research and development department has launched many innovative and unique products in recent years. Many of these innovations have been developed together with our customers.

Bathing order
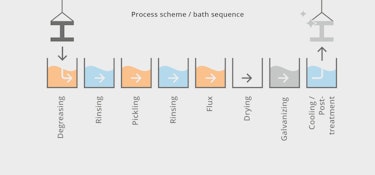
The galvanising process (batch galvanising) usually follows a fixed pattern:
Degreasing bath: The components are prepared in a degreasing bath with an aqueous alkaline or acidic degreasing agent.
Rinsing step: The subsequent rinsing step prevents the degreasing solution from being carried over into the subsequent baths.
Pickling bath: In the pickling bath, diluted hydrochloric acid removes scale, rust and other inherent impurities from the components. A setting with the right additives increases the service life of the bath and protects the components
Rinsing step: A further rinsing step prevents pickling solution from being carried over into the subsequent baths.
Flux bath: A flux bath usually contains an aqueous salt solution of zinc chloride and ammonium chloride. Fluxing increases wettability and prepares the component surface for contact with the liquid zinc in the tank.
Drying: The flux film is dried on the component.
Galvanising bath: In the galvanizing kettle, the component is immersed in a molten zinc alloy, creating an iron-zinc alloy layer.
Post-treatment bath and Cooling: Final cooling in the air or in a water bath. In the post-treatment bath, the component is given a protective coating that improves the corrosion resistance of the zinc coating and prevents white rust formation.
Service & Support
Our experts in Europe







